Attention
This document is no longer being updated. For the most recent documentation, including the latest release notes for version 6, please refer to Documentation Version 7
Business Rules
This is the layer where your business logic will be applied to the data. It is a second layer on top of the business object, which can then be fed to the accesslayer. The business logic will be applied in the form of a database view. This enables you to make use of any functionality of the underlying database.
- Definition
A business ruleset is a view on top of a business object. It allows the application of custom business logic.
Note
For auditability or performance reasons, it can sometimes make sense to loop back the data and persist it in the data vault. This procedure is called Business Vault.
- Search Bar
Filters the business ruleset list.
- Business Ruleset List
Lists the existing business rulesets. Grouped by Business Object > System. Select a business ruleset from the list to see and edit its code with the editor.
- Business Ruleset Editor
- The editor displays the SQL-Code of the view and allows implementation of new business logic.The
 next to it (de-)activates the data preview of the result at the bottom.
next to it (de-)activates the data preview of the result at the bottom.- Often used Keyboard-Shortcuts:
Action
Windows/Linux
Mac
Find
Ctrl-F
Cmd-F
Replace
Ctrl-H
Cmd-Option-F
Fold
Alt-L
Cmd-Option-L
Go to Line
Ctrl-L
Cmd-L
Remove line
Ctrl-D
Cmd-D
Move line up, down
Alt-Up, Alt-Down
Option-Up, Option-Down
- Add Business Ruleset
Opens up the creation dialogue for adding a business ruleset.
- Business Ruleset Properties
Clicking onto the
 opens up the slider from the left, containing the business ruleset properties.
opens up the slider from the left, containing the business ruleset properties.
- Quick Inserts
- Quick inserts can be used to search for tables/views on the database you would like to join to.This panel is made up of a search box at the top and a list of tables/views.
You can add more entries to the list using the search field.
Expand the name of the available list entries to see the fields available within the object.
Use the plus-icon or double-click to add the element to the view.
Adding Business Rules
To be able to add a business ruleset, an underlying business object needs to be created first.
- Steps
Navigate to the Business Rules module and click onto “Add Business Ruleset”. Alternatively, you can click onto
 in the business ruleset list. This will automatically complete the first two fields of the creation dialogue.
in the business ruleset list. This will automatically complete the first two fields of the creation dialogue.Complete the creation dialogue.
Modify the view code in the editor to implement business logic.
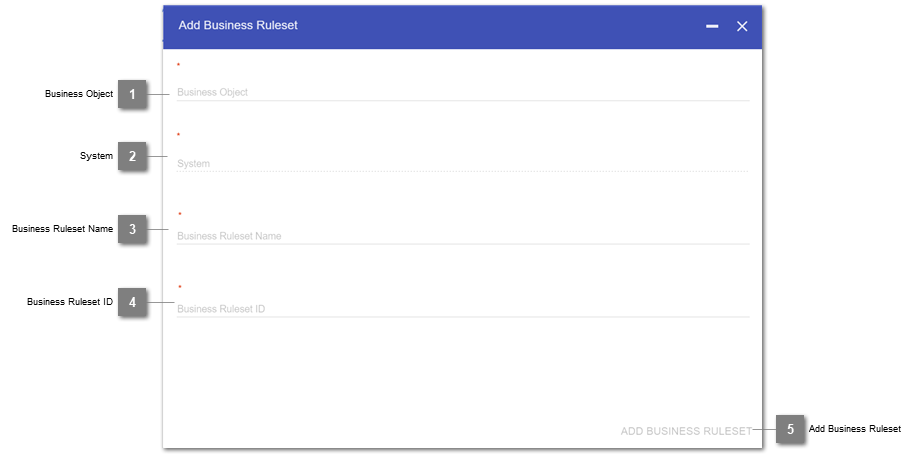
- Business Object
Selection of the underlying business object to build the business ruleset on top of.
- System
Declaration of the source system, to define, for which related business object the rule should be created.
- Business Ruleset Name
Displayed name of the newly created business ruleset.
- Business Ruleset ID
Technical suffix ID for the business ruleset, which will be added to the view-name on the database.
- Add Business Ruleset
Button to complete the business ruleset creation.
Business Ruleset Properties
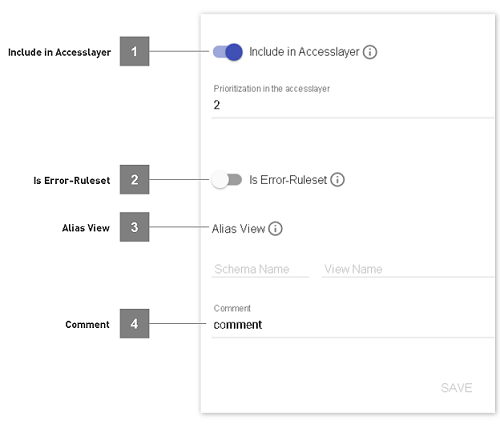
- Include in Accesslayer
The button toggles, whether the specific business ruleset is fed into the accesslayer. If enabled, a priorization can be given. The priorization is used, when combining different business rulesets in the accesslayer:
When a positive number is defined for the priorization for two or more business rulesets and if these rulesets have a different result for a field, then the value of the priorized business ruleset or the first non-null value is taken (golden record selection).
When a priorization of -1 is specified, then no golden record selection is performed for this business ruleset (e.g. the business ruleset is combined using a UNION ALL in the corresponding accesslayer).
Hint
This means, if there are three business rulesets, the first two having a positive priorization and the last has a priorization of -1, then for the first two the golden record selection is applied and the result is combined (using a UNION ALL) with the last business ruleset.
- Is Error-Ruleset
Defines the ruleset to be an error-view. The error-view will be mirrored into the errormart, as well as combined into an accesslayer-like errormart-view.
- Alias View
Create an alias view (schema_name.view_name) on the database to mirror this business ruleset. When choosing a custom schema, make sure that the schema exists and dvb_user/dvb_admin have the grants to manage views in it. May not be one of staging, datavault_staging, datavault, business_rules, businessobjects. If alias_schema_id is accesslayer, best practice is to use same view_nq_id as business rule (this way stays unique).
- Comment
Custom notes about the business ruleset
Deleting a Business Ruleset
- Steps
- The deletion of a business ruleset will:
Delete the business ruleset view
Remove the business ruleset from the accesslayer (if fed into the accesslayer)
Remove the error-mart view (if declared as error-ruleset)
Remove the alias view (if declared having an alias view)
Limitations
On Exasol, a business rule may not contain a “;” besides the one ending the view code (others will be removed automatically on save by the database).